| Issue |
Details and Discussion |
| Status of Regulation |
| Legal Status |
California Air Resources Board (CARB) adopted final regulations on October 20, 2011. The regulation has been amended periodically since then. The legislature authorized an extension of the program (AB 398) through 2030 in 2017. Pursuant to this extension, CARB amended the program regulation at the end of 2018 in order to address cost containment, offsets, allocation, phase-out of exemptions, administrative issues, and the delinking with Ontario. |
| Regulation Coverage |
| Threshold of Coverage |
Sources that emit at least 25,000 metric tons CO2e/year are subject to regulation, including importers of electricity to the state. |
| Gases Covered |
The six gases covered by the Kyoto Protocol (CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs, PFCs, SF6),
plus NF3 and other fluorinated greenhouse gases |
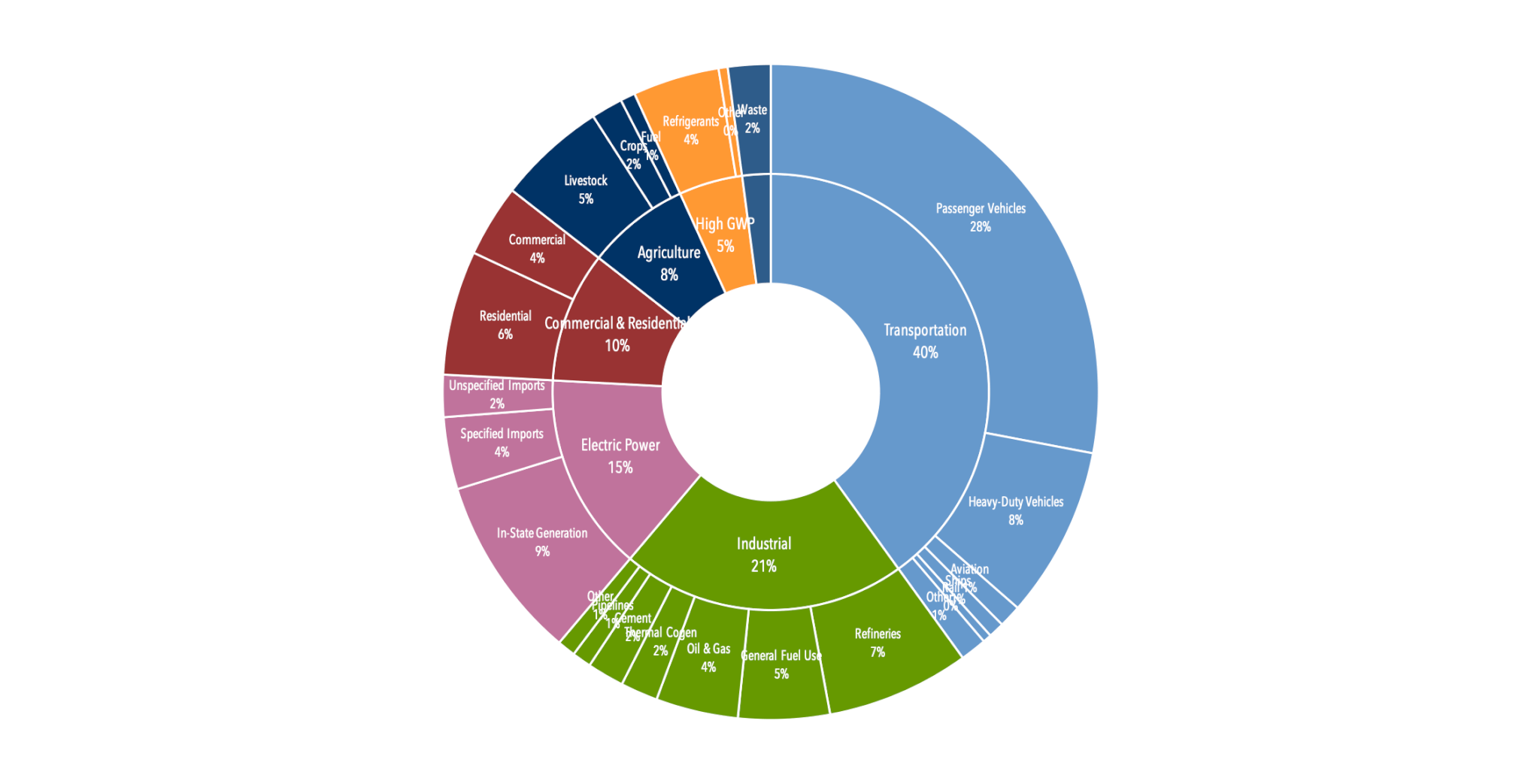
| Sectors Covered: Phase 1 (2013-2014) |
Electricity generation, including imports
industrial sources |
| Sectors Covered: Phase 2 (2015-onward) |
Includes sectors covered in Phase 1, plus:
Distributors of petroleum
Distributors of natural gas |
| Point of Regulation |
Electricity generators (within California)
Electricity importers
Industrial facility operators
Fuel distributors |
| Allowance Allocation |
| Distribution Method |
Free allocation for electric utilities, industrial facilities and natural gas utilities (investor-owned utilities must sell free allowances and redistribute funds to customers)
Free allocation to utilities declines over time
Other allowances must be purchased at auction or via trade |
| Allocation Methodology |
Industry: Based on output and sector-specific emissions intensity benchmark that rewards more efficient facilities
Electricity: Based on long-term procurement plans
Natural gas: Based on 2011 sales |
| Auction |
Quarterly, single round, sealed bid, uniform price
Price minimum: Began at $10 in 2012 and increases 5% annually over inflation
Price maximum: Additional allowances are available for sale when prices reach an upper threshold, set at $40 in 2012, increasing 5% annually over inflation. Beginning in 2021, a hard price ceiling of $65 will be set, increasing 5% annually (adjusted for inflation), and an unlimited supply of allowances will be available at this price
Investor-owned utilities must consign their free allowances to be sold at auction; must use proceeds for ratepayer benefitAdditional information, including auction results, can be found here |
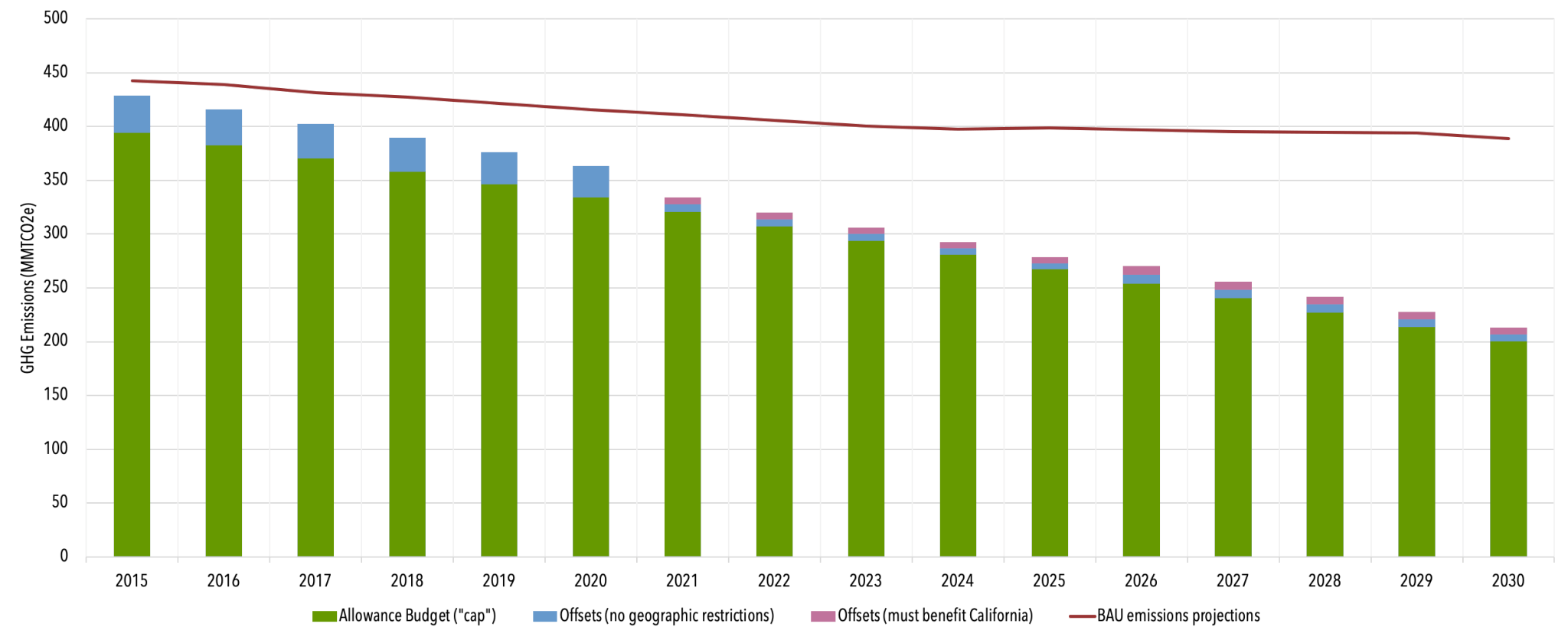
| Emission Targets / Allowance Budget |
162.8 MMT in 2013 (electricity and industry)
394.5 MMT in 2015 (includes all covered sectors)
334.2 MMT in 2020
200.5 MMT in 2030
(See Figure 2 below) |
| Compliance Flexibility |
| Banking |
A participating entity may bank allowances for future use and these allowances will not expire. However, regulated entities are subject to holding limits, restricting the maximum number of allowances that an entity may bank at any time. The holding limit quantity is based on a multiple of the entity’s annual allowance budget. |
| Borrowing |
Borrowing of allowances from future years is not allowed. |
| Offsets: Quantity |
Allowed for 8% of total compliance obligation through 2020; 4% between 2021 and 2025; 6% between 2026 and 2030. Beginning in 2021 at least half the offsets used for compliance must come from projects that directly benefit California. |
| Offsets: Protocols |
Offsets must comply with CARB-approved protocols. Protocols currently exist for: forestry (including urban forestry), dairy digesters, ozone depleting substances projects, mine methane capture, and rice cultivation. Offset projects may be located anywhere in the U.S. All offset projects developed under a CARB Compliance Offset Protocol must be listed with an ARB approved Offset Project Registry. |
| Strategic Reserve |
A percentage of allowances is held in a strategic reserve by CARB in three tiers with different prices: $62.29, $70.09, and $77.86 in 2020, rising 5% annually plus inflation. The strategic reserve will help constrain compliance costs by adding supply to the market when prices would otherwise be above the tiers. |
| Compliance Period |
3-year compliance periods (following 2-year Phase 1), with a partial surrender obligation due each year. |
| Emissions Reporting and Verification |
| Reporting |
Covered entities must report annually (as required since 2008). |
| Registration |
Covered entities and other participants must register with CARB to participate in allowance auctions. |
| Verification |
Reported emissions must be verified by a third party. |
| Compliance and Enforcement |
| Annual Obligation |
Entities must provide allowances and/or offsets for 30% of their previous year’s emissions each year. |
| Compliance Period Obligation |
At the end of every multi-year compliance period, entities must provide allowances and/or offsets for the balance of emissions from the entire compliance period. |
| Noncompliance |
If a deadline is missed or there is a shortfall, four allowances must be surrendered for every metric ton not covered in time. |
| Trading and Enforcement |
The regulation expressly prohibits any trading involving a manipulative device, a corner of or an attempt to corner the market, fraud, attempted fraud, or false or inaccurate reports.
Violations of the regulations can result in civil or criminal penalties. Perjury statutes apply.
The program includes mechanisms to monitor for and prevent market manipulation. |
| Linking |
| Direct linkages |
California’s program linked with Quebec’s program on January 1, 2014, and Ontario’s program on January 1, 2018, but unlinked with the latter following Ontario’s discontinuation of its program in mid-2018. Offsets and allowances can be traded across jurisdictions. The linked jurisdictions hold joint auctions together. |
| Indirect linkages |
California has a memorandum of understanding with the Mexican state of Chiapas and the Brazilian state of Acre to develop sector-based offsets from projects that reduce emissions from deforestation and land degradation (REDD). A working group submitted recommendations for REDD protocols, though no REDD compliance protocols have been approved by CARB.
Washington state’s Climate Commitment Act could accept allowances from out-of-state programs for a facility’s compliance obligation. Washington’s Department of Ecology will begin a rulemaking process for the Climate Commitment Act. The rulemaking process could identify which carbon market(s)’s allowances would be eligible, and California is one possibility. If out-of-state buyers entered the market for California allowances, it could affect prices for California entities through an indirect linkage. |