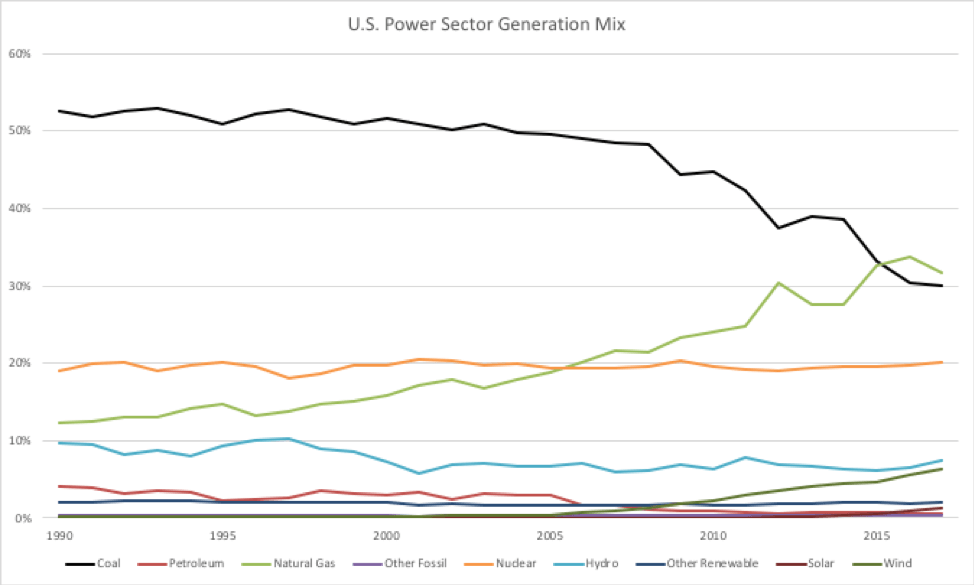
Since 2005, renewable generation has accelerated, particularly wind generation, though solar is growing more quickly now too. A range of federal, state, local, and business support have helped expand the market and ultimately lower prices for wind and solar. In 2005, wind and solar contributed less than one-half of one percent of the generation mix. In 2017, they contributed 8 percent of total generation.
One troubling trend is the declining state of nuclear power. Nuclear power plants have consistently delivered 20 percent of the total electricity mix and provided more than 50 percent of all zero-emission electricity. However, these large sources of zero-emission power are being prematurely retired with respect to their operating licenses because of low wholesale electricity prices resulting from low natural gas prices, excess power generation capacity, declining renewable energy costs, and low growth in electricity demand. When one closes prematurely, it is not a simple matter to replace it quickly with non-emitting alternatives. Rather, nuclear generation is largely being replaced by fossil fuel-fired electricity, threatening the trajectory of U.S. emissions. Fortunately, states are taking the lead in preventing premature nuclear power plant closures.
In order to meet the 2-degree Celsius (3.8-degree Fahrenheit) target agreed to by the international community and avoid the worst effects of climate change, global net greenhouse gas emissions must be approaching zero by the second half of this century. Pathways to deep decarbonization generally focus on three, equally important strategies for our energy system:
(1) increasing deployment of energy efficiency, (2) decarbonization of the energy supply, and (3) fuel switching. Among the energy supply decarbonization strategies, there are many possible ways to decarbonize the power sector. However, most studies indicate that a diverse mix of renewables, nuclear power, and fossil fuel with carbon capture utilization and storage is the least costly and least technically challenging path to achieve the mid-century goal.
There is still much work to do to reduce power sector emissions by more than 80 percent by 2050. The current business-as-usual policy approach will not achieve the necessary reductions. In order to preserve and accelerate the downward trend in carbon dioxide emissions, policy solutions are needed to encourage lower and zero-emission energy sources and to encourage energy efficiency to reduce demand. Since fossil fuels – whether natural gas or coal – will continue to comprise a significant portion of power generation well into the future, it also makes sense to continue to support government and industry work toward commercialization of carbon capture and storage technologies.
With continuing growth of solar and wind, lower-emitting natural gas (relative to decades of coal use), and some states enacting policies to preserve nuclear generation we seem to be trending back in time as far as energy emissions go. But policy solutions are needed to support existing nuclear power in other states, help set the stage for advanced nuclear and carbon capture, and expand renewables for a much cleaner second-half of this century. We cannot be short-sighted; we need a comprehensive long-term strategy in order to realize our low-carbon future.
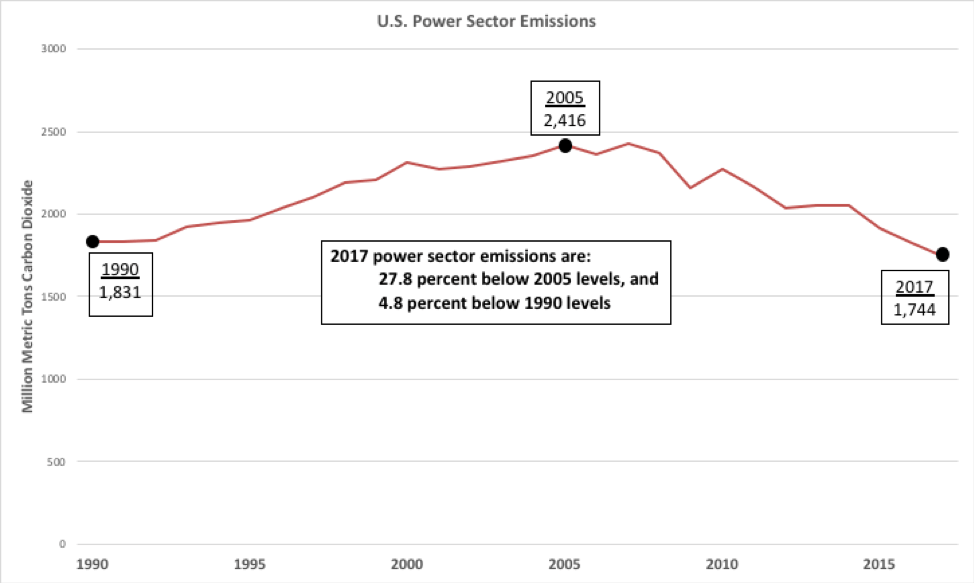
Five years ago, I blogged on emission levels reaching 1994 levels (Party like it’s 1994). As progress continues, I’ll hope to offer a disco flashback for the next installment.