How significant a source of emissions is air travel?
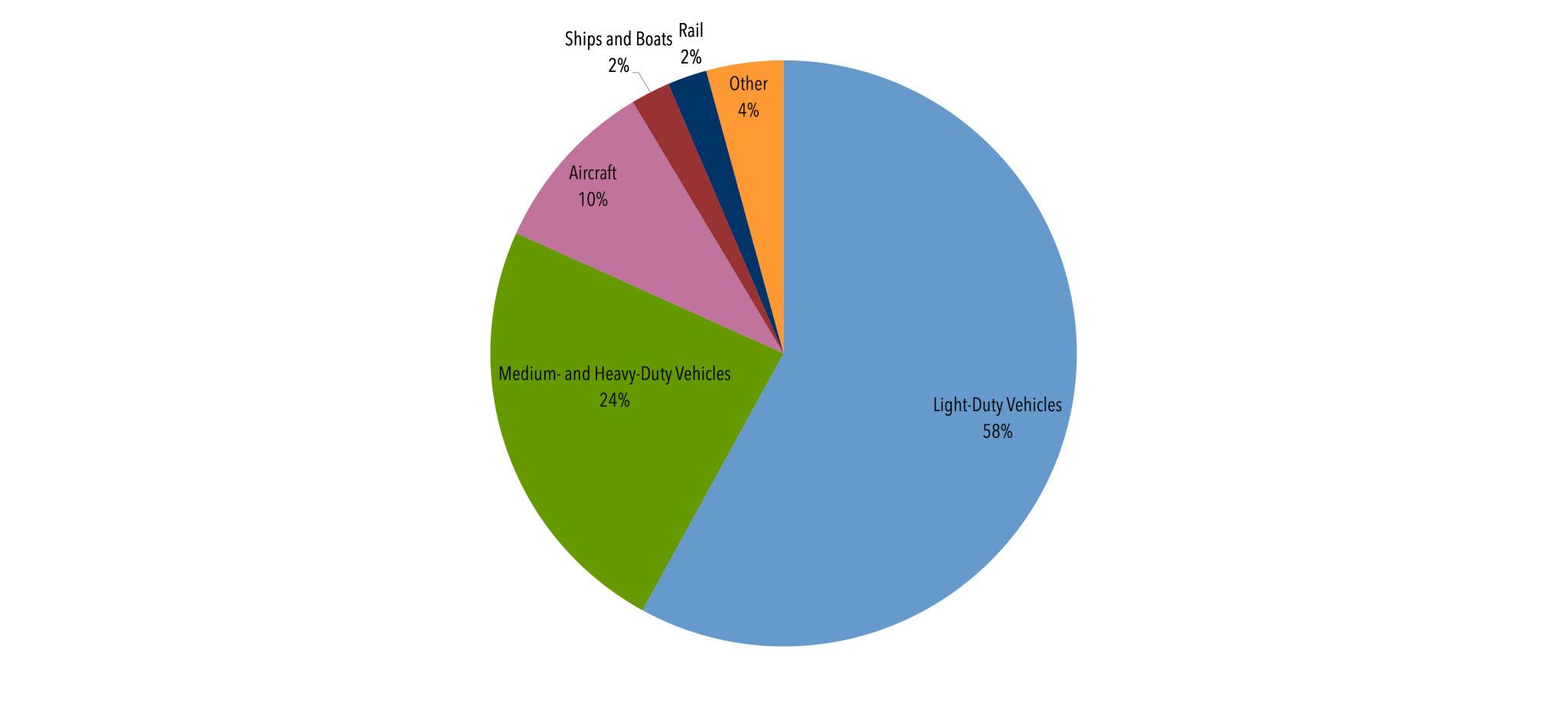
Aircraft are a rapidly growing emissions source within the transportation sector, which has surpassed the power sector as the biggest source of U.S. carbon dioxide emissions. In 2018, aircraft were responsible for about 3 percent of total U.S. carbon dioxide emissions and nearly 9 percent of greenhouse gas emissions from the U.S. transportation sector. Commercial air travel accounted for most of the aircraft carbon dioxide emissions, with military and general aviation making up the rest.
From 1990 to 2018, U.S. carbon dioxide emissions from domestic commercial flights grew about 18 percent. Recent studies estimate that U.S. aircraft emissions will increase substantially in the next 20 years. Moreover, airplanes remain the single largest source of carbon dioxide emissions within the U.S. transportation sector that is not yet subject to federal greenhouse gas regulations.
U.S. aviation is part of the increasingly interconnected global aviation sector, which makes up more than 2 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions but is one of the fastest growing sources. From 1990 to 2010, global aircraft carbon dioxide emissions grew about 40 percent. From 2013 to 2018, global emissions grew another 26 percent. If global aviation were a country, it would rank as the 20th largest carbon dioxide emitter, and U.S. aircraft emissions are 24 percent of all global aircraft emissions. Absent new policies, global aircraft emissions are projected to triple by 2050.