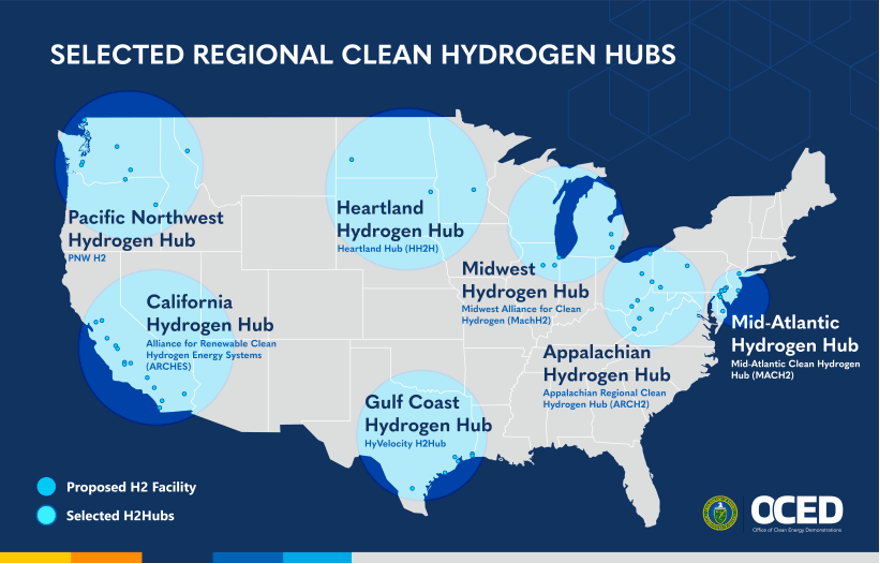
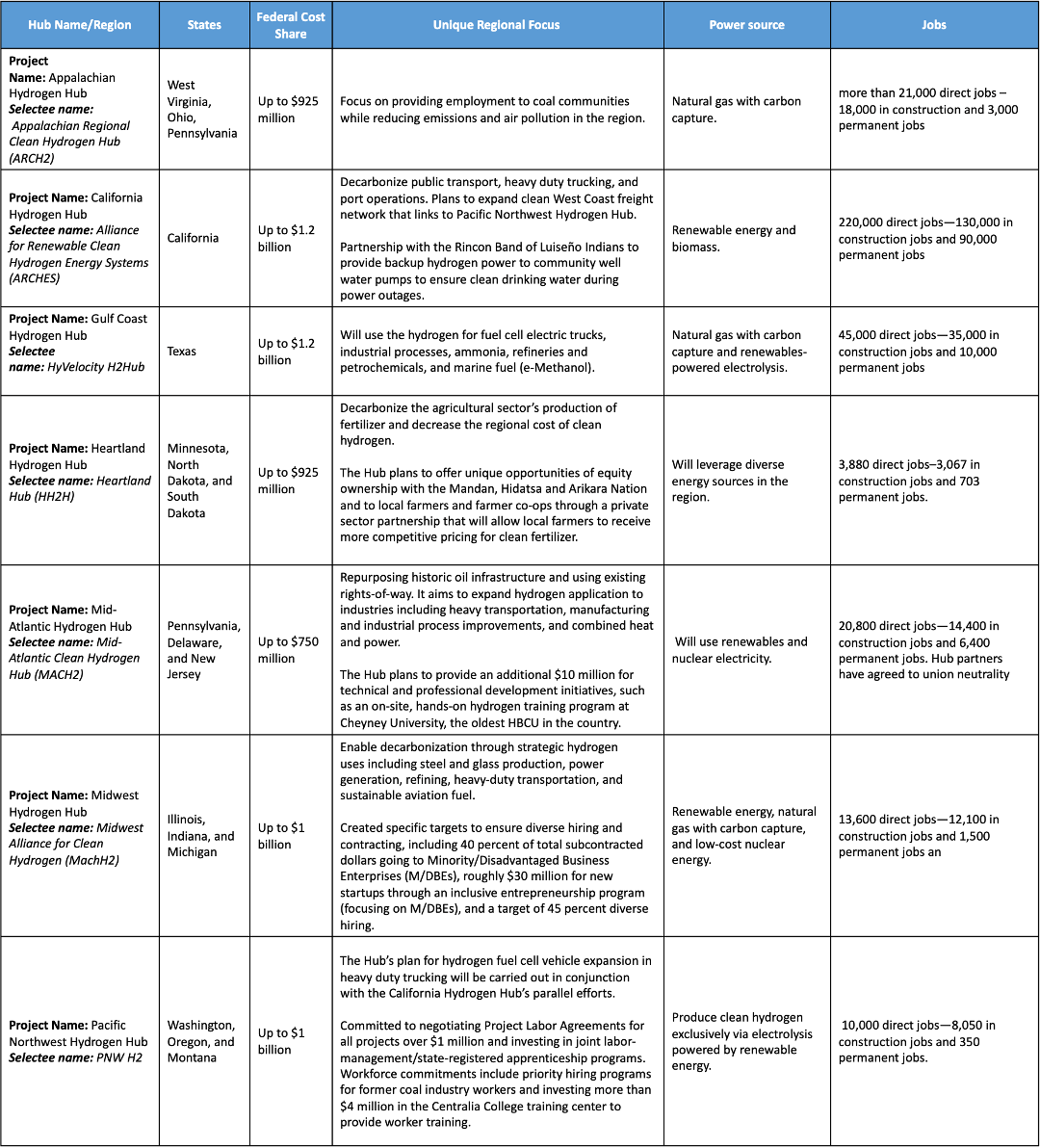
The Department of Energy recently announced $7 billion to launch seven Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs (H2Hubs) across the United States to accelerate commercialization and deployment of clean hydrogen. The energy transition will necessarily look different in different communities; by flexibly supporting the unique and innovative design of each of the selected hubs, this public investment is poised to deliver results that reflect the strengths, interests and capacities of the regions where they’re located.
The Hydrogen Hubs are regional networks of clean hydrogen producers, consumers, and connecting infrastructure. Clean hydrogen has multiple production pathways, including via electrolysis using renewable or nuclear energy. It can also be produced via steam methane reforming using natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS). It is a highly versatile resource and can be used to tackle hard-to-decarbonize sectors like industrial manufacturing and long-haul heavy-duty transportation. The hub model addresses some of the key market challenges for hydrogen, with shared infrastructure and co-located demand helping to develop an entire hydrogen ecosystem in a region.
Each hydrogen hub reflects unique characteristics of the surrounding communities. For example, California’s Hydrogen Hub will focus on decarbonizing transportation, which is a major source of air pollution and emissions in the state. By contrast, the Midwestern Heartland Hydrogen Hub will focus on decarbonizing agricultural fertilizer and offering equity ownership opportunities for tribal nations and local farmers.